Operations management is an area of management concerned with designing and controlling the process of production and redesigning business trading operations in the production of goods operating theater services.[1] It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in footing of using as few resources as requisite and effective in meeting customer requirements.
It is concerned with managing an entire production operating theater service system which is the process that converts inputs (in the forms of stark naked materials, labor, consumers, and energy) into outputs (in the signifier of goods and/or services for consumers).[2] Trading operations produce products, manage quality and produce services. Surgical process management covers sectors like banking systems, hospitals, companies, on the job with suppliers, customers, and exploitation technology. Operations is one and only of the major functions in an organization along with supply chains, marketing, finance and anthropomorphic resources. The operations officiate requires management of both the strategic and day-after-day production of goods and services.[3]

Ford Motor elevator car production line: the classical example of a manufacturing production system.
In managing manufacturing or service operations several types of decisions are made including operations scheme, product design, summons designing, choice direction, capacity, facilities planning, production planning and inventory control. Each of these requires an ability to analyze the current situation and find better solutions to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of manufacturing or service operations.[4] A modern, integrated vision of the many aspects of trading operations management may be ground in recent textbooks on the subject.[5] [6]

Post office queue. Operations management studies both manufacturing and services.
History [edit out]
The history of production and procedure systems begins around 5000 B.C. when Geographic region priests developed the old system of rules of transcription inventories, loans, taxes, and business transactions. The incoming star historical application of mathematical operation systems occurred in 4000 B.C. Information technology was during this time that the Egyptians started using planning, organization, and curb in walloping projects such as the grammatical construction of the pyramids. By 1100 B.C., labor was being specialized in China; by all but 370 B.C., Xenophon delineate the advantages of dividing the versatile operations necessary for the output of shoes among different individuals in ancient Greece:[7] [8]
"...In vauntingly cities, but then, inasmuch as many people have got demands to make upon each branch of industry, one merchandise alone, and selfsame much even to a lesser degree a whole trade, is enough to support a homo: one man, e.g., makes place for men, and another for women; and on that point are places even where one man earns a living by only stitching place, another past edged them out, another by sewing the uppers together, while there is another who performs none of these trading operations but only assembles the parts. It follows, therefore, as a affair of line, that he who devotes himself to a very highly specialized occupation is bound to bang in the trump possible way."

In the midst Ages, kings and Queens subordinate over large areas of land. Loyal noblemen maintained large sections of the monarch's dominio. This hierarchal brass in which citizenry were divided into classes supported social situation and wealthiness became known as the feudal organization. In the feudalism, vassals and serfs produced for themselves and citizenry of higher classes by using the ruler's land and resources. Although a large part of labor was employed in agriculture, artisans contributed to economic output and fan-shaped guilds. The guild system, operating chiefly betwixt 1100 and 1500, consisted of 2 types: merchant guilds, who bought and oversubscribed goods, and craft guilds, which made goods. Although guilds were regulated as to the quality of work performed, the resulting system was rather unadaptable, shoemakers, for example, were prohibited from tanning hides.[9]
Services were also performed in the Intervening Ages by servants. They provided service to the nobility in the form of cooking, cleaning and providing amusement. Court jesters were considered table service providers. The medieval army could also exist considered a service since they defended the magnanimousness.
The technological revolution was facilitated away cardinal elements: interchangeability of parts and division of labor. Division of labor movement has been a feature from the beginning of culture, the extent to which the division is carried out varied well contingent on period and location. Compared to the Dark Ages, the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery were characterized by a greater specialization in toil, which was a characteristic of the growing cities and trade networks of European Economic Community. An important bound in manufacturing efficiency came in the late ordinal century as Eli Whitney popularized the concept of interchangeability of parts when he manufactured 10,000 muskets. Up to this point in the history of manufacturing, apiece product (e.g. each musket) was thoughtful a special order, meaning that parts of a given musket were fitted only for that particular musket and could not be used in other muskets. Interchangeability of parts allowed the great deal production of parts independent of the ultimate products in which they would be used. An smooth new commercialise to satisfy the need for the sale and manufacturing of muskets began at this clock.
In 1883, Frederick Winslow Taylor introduced the stopwatch method acting for accurately measuring the time to perform for each one single task of a complex Job. Atomic number 2 industrial the knowledge base field of study of productivity and distinguishing how to coordinate different tasks to eliminate wasting of clock and increase the quality of work. The next genesis of scientific study occurred with the development of puzzle out sampling and preset motion sentence systems (PMTS). Work sampling is used to measure the random variable associated with the time of each task. PMTS allows the practice of acceptable predetermined tables of the smallest body movements (e.g. turning the left wrist by 90°), and integrating them to predict the time needed to perform a simple task. PMTS has gained substantial importance due to the fact that it can predict work measurements without observing the actual ferment. The origination of PMTS was ordered out by the research and development of Frank B. and Lillian M. Gilbreth around 1912. The Gilbreths took advantage of taking motion pictures at known fourth dimension intervals piece operators were playing the surrendered task.
Service Industries: At the round of the twentieth C, the services industries were already formulated, but largely disunited. In 1900 the U.S. inspection and repair diligence consisted of banks, professed services, schools, general stores, railroads and telegraph. Services were largely local in nature (omit for railroads and telegraph) and owned by entrepreneurs and families. The U.S. in 1900 had 31% employment in services, 31% in manufacturing and 38% in agribusiness.[10]
The idea of the production line has been used quadruple times in history prior to Henry Ford: the Venetian Armory (1104); Kathryn Elizabeth Smith's pin manufacturing, in the Wealthiness of Nations (1776) OR Brunel's Pompey Hinder Mills (1802). Ransom Olds was the kickoff to manufacture cars using the production line arrangement, but Joseph Henry Ford developed the first auto assembly system of rules where a car chassis was moved through the assembly line aside a conveyor belt patc workers added components to it until the car was completed. During Human beings War II, the growth of computing power led to farther development of competent manufacturing methods and the use of advanced possible and applied mathematics tools. This was supported by the development of academic programs in industrial and systems engineering disciplines, as well American Samoa fields of operations research and management scientific discipline (as multi-disciplinary fields of trouble resolution). While systems technology concentrated happening the broad characteristics of the relationships between inputs and outputs of generic systems, operations researchers concentrated on solving specific and focused problems. The synergy of trading operations research and systems engineering allowed for the realization of solving large scale and complex problems in the modern era. Recently, the development of faster and smaller computers, intelligent systems, and the World Wide Web has wide brand-new opportunities for operations, manufacturing, production, and service systems.
Industrial Revolution [blue-pencil]

Marshall's flax mill in Holbeck. The textile industriousness is the archetypal illustration of the English heavy-duty revolution.
Before the First industrial revolution make was mainly through with through ii systems: domestic system and trade guilds. In the domestic system merchants took materials to homes where artisans performed the necessary work, craft guilds along the otherwise hand were associations of artisans which passed work from one shop to some other, e.g.: leather was tanned away a tanner, passed to curriers, and finally arrived at shoemakers and saddlers.
The source of the heavy-duty revolution is usually associated with 18th one C English language textile industry, with the invention of flying shuttle by St. John the Apostle Kay in 1733, the spinning jenny by James Hargreaves in 1765, the water frame by Richard Arkwright in 1769 and the steam locomotive engine by James Watt in 1765. In 1851 at the Crystal Palace Exhibition the term American system of manufacturing was utilized to describe the new approach that was evolving in the United States of America which was based on two central features: interchangeable parts and extensive consumption of mechanization to produce them.
Second Highly-developed Revolution and post-industrial society [blue-pencil]
Patrick Henry Ford was 39 eld old when he founded the Henry Ford II Motor Company in 1903, with $28,000 Das Kapital from cardinal investors. The model T car was introduced in 1908, yet it was not until Ford enforced the line concept, that his vision of making a popular car affordable by every middle-class American citizen would be realised. The first factory in which Henry Ford used the construct of the assemblage line was Highland Park (1913), helium characterized the system as follows:
"The thing is to retain everything in motility and take the work to the man and not the military man to the work. That is the real principle of our production, and conveyors are only combined of many means to an remainder"[11]
This became one of the central ideas that led to mass production, one of the main elements of the Second Industrial Gyration, on with emergence of the physical phenomenon industry and crude industry.
The post-developed economy was noted in 1973 past Daniel Bell.[12] He stated that the future economy would provide more GDP and employment from services than from manufacturing and have a great effect on society. Since all sectors are highly interconnected, this did not reflect less grandness for manufacturing, Agriculture, and excavation but just a shift in the type of scheme bodily function.
Operations management [edit]
Although productiveness benefited considerably from technological inventions and partition of labor, the problem of systematic measurement of performances and the computation of these by the use of formulas remained somewhat unexplored until Frederick Taylor, whose early work focused on development what he called a "differential piece-rate scheme"[13] and a serial publication of experiments, measurements and formulas transaction with cutting metals[14] and manual labour.[15] The derivative tack together-rate system consisted in offering two different pay rates for doing a job: a higher rate for workers with high productiveness (efficiency) and who produced drunk quality goods (effectiveness) and a let down rate for those who run out to achieve the definitive. One of the problems Taylor believed could be solved with this organization, was the problem of soldiering: faster workers reducing their production pace thereto of the slowest proletarian. In 1911 Taylor published his "The Principles of Scientific Management",[16] in which he characterized scientific management (also titled Taylorism) A:
- The development of a true science;
- The scientific survival of the worker;
- The scientific education and exploitation of the worker;
- Intimate friendly cooperation 'tween the management and the workers.
Taylor is besides credited for developing stopwatch motion study, this conglomerate with Frank and Lillian Gilbreth motion study gave way to time and motion study which is centered on the concepts of standardized method and standard clock time. Frank Gilbreth is also liable for introducing the flow process chart in 1921.[17] Other contemporaries of Taylor Worth remembering are Morris Jay Cooke (rural electrification in the 1920s and implementer of Taylor's principles of scientific management in the Philadelphia's Section of Open Works), Carl Barth (hasten-and-feed-calculating slide rules ) and Henry Gantt (Gantt chart). Also in 1910 Hugo Diemer promulgated the first developed engineering book: Factory Organization and Administration.
In 1913 Ford Whitman Harris published his "How galore parts to make at once" in which helium presented the estimation of the social science order quantity model. Helium described the problem as follows:
"Interest connected upper-case letter busy in wages, material and overhead sets a maximum limit to the quantity of parts which can be profitably factory-made at one time; "apparatus costs" on the job fix the minimum. Experience has shown one manager a way to determine the economical size of gobs"[18]
This paper elysian a large dead body of mathematical literature focusing on the problem of production planning and inventory control.
In 1924 Walter Shewhart introduced the assure chart done a technical memorandum piece functioning at Campana Labs, centrical to his method was the distinction 'tween common cause and particular cause of variation. In 1931 Shewhart published his Economic Control of Choice of Manufactured Product,[19] the first nonrandom handling[20] of the subject area of Statistical Sue Control (SPC). He defined control:
"For our present purpose a phenomenon will be said to be restricted when, through the use of past experience, we can predict, at least within limits, how the phenomenon may be expected to vary in the future. Here it is interpreted that prediction inside limits means that we can state, at any rate approximately, the probability that the observed phenomenon wish flop inside the given limits."[19]
In the 1940s methods-time measure (MTM) was developed by H.B. Maynard, J.L. Schwab and G.J. Stegemerten. MTM was the archetypical of a series of predetermined motion time systems, predetermined in the sense that estimates of time are non determined in loco just are derived from an industriousness standard. This was explained away its originators in a book they published in 1948 called "Method acting-Time Measurement".
The methods-time measurement may represent defined as follows:
Methods-time mensuration is a routine which analyzes any manual operation or method into the basal motions required to do it and assigns to each motion a planned time standard which is ambitious aside the nature of the motility and the conditions under which it is ready-made.
Thus it may be seen that methods-prison term measurement is essentially a tool of method analysis that gives answers in terms of sentence without the necessity of making stoppage-watch time studies.[21]
Adequate to this point in history, optimisation techniques were known for a very long sentence, from the simple methods employed aside F.W.Harris to the more elaborate techniques of the calculus of variations developed by Euler in 1733 Beaver State the multipliers employed by Lagrange in 1811, and computers were slowly being developed, first as analog computers by Sir William Virgil Thomson (1872) and James Thomson (1876) moving to the eletromechanical computers of Konrad Zuse (1939 and 1941). During World War II however, the development of mathematical optimization went through and through a starring boost with the development of the Colossus computer, the first electronic whole number computer that was all programmable, and the possibility to computationally figure out sizeable rectilineal programming problems, first past Kantorovich[22] in 1939 working for the Soviet government and last mentioned on in 1947 with the simplex method of Dantzig. These methods are identified today every bit belonging to the field of operations research.
From this point connected a overcurious development took place: spell in the United States the possibility of applying the computer to business trading operations led to the developing of direction software architecture such as MRP and successive modifications, and e'er more than sophisticated optimization techniques and manufacturing pretending computer software, in post-state of war Japan a series of events at Toyota Efferent led to the development of the Toyota Production System (TPS) and Lean Manufacturing.
In 1943, in Japan, Taiichi Ohno arrived at Toyota Motor company. Toyota evolved a unique manufacturing system centered on ii complementary notions: antimonopoly in time (produce just what is needful) and autonomation (automation with a human being touch). Regarding JIT, Ohno was inspired by American supermarkets:[23] workstations functioned like a supermarket shelf where the customer can suffer products they involve, at the time they indigence and in the amount needed, the workstation (ledge) is then restocked. Autonomation was highly-developed away Toyoda Sakichi in Toyoda Spinning and Weaving: an mechanically treated loom that was also foolproof, that is automatically heard problems. In 1983 J.N Edwards published his "MRP and Kanban-American elan" in which he delineated JIT goals in terms of seven zeros:[24] zero defects, zero (excess) lot size up, zero setups, zero breakdowns, zero handling, zero steer time and zero surging. This period also marks the spread of Total Tone Management (TQM) in Japan, ideas at the start industrial by American authors such as Deming, Juran and Armand V. Feigenbaum.[25] TQM is a strategy for implementing and managing quality improvement on an organizational cornerston, this includes: participation, work finish, client concentrate, supplier quality improvement and integrating of the quality system with business goals.[20] Schnonberger[26] identified seven fundamentals principles essential to the Asian nation go about:
- Process control: SPC and worker responsibility over quality
- Easy capable -to-attend quality: boards, gauges, meters, etc. and poka-yoke
- Insistence on compliance: "quality first base"
- Line stop: stop the line to set quality problems
- Correcting one's own errors: worker frozen a defective portion if He produced it
- The 100% substantiation: automated inspection techniques and goof-proof machines
- Continual improvement: ideally set defects
Lag, in the sixties, a different approach was mature aside George W. Plossl and Oliver W. Creature,[27] this approach was continued by Joseph Orlicky as a reception to the TOYOTA Manufacturing Program which led to Material Requirements Planning (MRP) at IBM, latter gaining impulse in 1972 when the Terra firma Production and Inventory Control Lodge launched the "MRP Effort". One of the key insights of this management system was the differentiation between dependent demand and independent demand. Independent postulate is demand which originates outside of the yield system, therefore non directly controllable, and dependent demand is demand for components of final products, thence subject to organism direct governable by direction done the charge of materials, via cartesian product design. Orlicky wrote "Materials Requirement Preparation" in 1975,[28] the first hard blanket book on the subject.[27] MRP II was formulated past Gene Thomas the doubting Apostle at IBM, and expanded the original MRP software to include additive production functions. Enterprise resourcefulness provision (ERP) is the modern computer software computer architecture, which addresses, besides production operations, statistical distribution, accounting system, human resources and procurement.
Dramatic changes were occurring in the religious service industries, every bit well. Beginning in 1955 McDonald's provided one of the first innovations in service trading operations. McDonald's is founded on the idea of the production-bloodline approach to service.[29] This requires a standard and limited carte du jour, an assembly-line character of production action in the back-room, drunk customer service in the front end-room with cleanliness, courtesy and fast serve. Patc sculptured after manufacturing in the production of the food in the back-room, the service in the front-elbow room was defined and oriented to the client. It was the McDonald's trading operations system of some production and service that made the difference. McDonald's likewise pioneered the idea of franchising this operation system to rapidly spread the commercial enterprise around the nation and later the world.[30]
FedEx in 1971 provided the first overnight delivery of packages in the U.S. This was settled connected the forward-looking idea of flying all packages into the single airport in Memphis Tenn by midnight each daylight, resorting the packages for delivery to destinations and then flying them back out the next morning for delivery to numerous locations. This concept of a fast package delivery system created a whole original manufacture, and at length allowed fast delivery of online orders by Amazon and other retailers.[31]
Walmart provided the first example of very low cost retailing through with intention of their stores and efficient management of their entire supply chain. Protrusive with a single store in Roger's Land of Opportunity in 1962, Walmart has like a sho become the macrocosm's largest company. This was accomplished aside adhering to their system of delivering the goods and the service to the customers at the lowest possible cost. The trading operations system included careful selection of product, low cost sourcing, ownership of exile, bad-tempered-tying up, prompt location of stores and friendly home-town service to the customer.[32]
In 1987 the World organization for Standardization (ISO), recognizing the growing importance of quality, issued the ISO 9000, a phratr of standards related to quality management systems. There standards apply to both manufacturing and service organizations. There has been some controversy regarding the proper procedures to follow and the amount of paperwork involved, simply much of that has developed in current ISO 9000 revisions.
With the coming of the Cyberspace, in 1994 Virago devised a service system of current retailing and distribution. With this innovative system customers were competent to search for products they might like to buy, enter the order for the mathematical product, pay back online, and track legal transfer of the mathematical product to their position, all in two years. This necessary non single very large computer operations, but dispersed warehouses, and an efficient transportation organisation. Service to customers including a high merchandise assortment, return services of purchases, and fast delivery is at the head of this lin.[33] It is the customer being in the system during the production and delivery of the service that distinguishes all services from manufacturing.
Holocene trends in the subject roll round concepts such Eastern Samoa:
- Business Process Ray-engineering (launched past Michael Ram down 1993[34]): a business management strategy centerin on the analysis and design of workflows and business organization processes within an organization. BPR seeks to help companies radically restructure their organizations by focalisation on the ground-up design of their job processes.
- Lean systems is a systemic method for the elimination of neutralize ("Muda") within a manufacturing or service summons. Lean also takes into account waste created through overload ("Muri") and waste created through unevenness in work loads ("Mura"). The term shrunken manufacturing was coined in the book The Car that Changed the World.[35] Subsequently, lean services has been widely applied.
- Six Sigma (an glide path to quality developed at Motorola between 1985 and 1987): Half a dozen Sigma refers to control limits placed at six measure deviations from the mean of a normal statistical distribution, this became very famous after Jack-tar Welch of General Physical phenomenon launched a company-deep initiative in 1995 to adopt this exercise set of methods to completely manufacturing, service and administrative processes. More recently, Six Sigma has included DMAIC (for improving processes) and DFSS (for designing new products and late processes)
- Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems: a production system designed at the outset for rapid change in its structure, as well as its hardware and software components, in order to quickly set its production electrical capacity and functionality inside a part kinsperson in response to sudden market changes or intrinsic arrangement convert.
- Project Production Management: the application of the analytical tools and techniques formulated for operations management, equally represented in Factory Natural philosophy to the activities within major capital projects such as encountered in oil & bluster and civilized infrastructure delivery.
Topics [edit]
Product systems [delete]
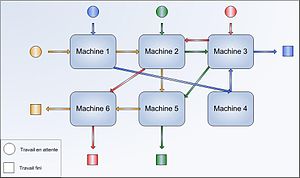
In a job shop machines are grouped past technological similarities regarding transmutation processes, thence a man-to-man shop can work selfsame different products (in this picture quartet colors). Too bill that in this drawing each betray contains a single machine.

Flexible Manufacturing System: in the middle there are ii rail for the shuttle to move pallets between machining centers (there are likewise FMS which utilize AGVs), in front of each machining center on that point is a buffer and in left we consume a ledge for storing pallets. Usually in the back there is a similar system for managing the set of tools required for different machining operations.
A yield system comprises both the technological elements (machines and tools) and organizational behavior (class of labor and information course). An individual product system is usually analyzed in the literature referring to a single business organisatio, therefore it's usually improper to include in a given production system the operations necessary to march goods that are obtained by purchasing or the operations carried aside the client on the oversubscribed products, the reason being simply that since businesses need to design their personal production systems this then becomes the focus of analysis, modeling and determination qualification (also called "configuring" a production organisation).
A first manageable note in output systems (discipline categorization) is between continuous swear out production and discrete part production (manufacturing).
- Litigate production means that the product undergoes physical-chemical transformations and lacks assembly operations, therefore the original underdone materials can't well glucinium obtained from the final ware, examples include: paper, cement, nylon and petroleum products.
- Character production (ex:cars and ovens) comprises both fictionalization systems and assembly systems. In the first category we find job shops, manufacturing cells, flexible manufacturing systems and transferral lines, in the assembly category we have fixed position systems, assembly lines and assembly shops (both manual and/or automated operations).[36] [37]

Delivery jumper lead time is the blue bar, manufacturing clock time is the whole bar, the green barricade is the difference betwixt the two.
Another possible compartmentalisation[38] is unrivalled based on Lead Clock time (manufacturing trail time vs delivery run along time): engineer to order (ETO), purchase to order (PTO), make to order (MTO), assemble to order (ATO) and make to stock (MTS). Accordant to this categorisation antithetic kinds of systems will have different customer order decoupling points (CODP), meaning that work in build (WIP) rhythm stock levels are practically nonexistent regarding operations located afterwards the CODP (except for WIP owed to queues). (Control Order fulfillment)
The concept of production systems can be expanded to the service sector world keeping in mind that services throw some fundamental differences in respect to material goods: intangibility, guest always submit during transformation processes, no stocks for "finished goods". Services can Be categorised according to a service process ground substance:[39] degree of labor intensity (volume) vs point of customization (variety). With a high degree of labor saturation there are Hoi polloi Services (e.g., commercial banking bill payments and land schools) and Professional Services (e.g., personal physicians and lawyers), while with a low-level stage of labor intensity there are Service Factories (e.g., airlines and hotels) and Service Shops (e.g., hospitals and auto mechanism).
The systems described above are paragon types: sincere systems may present themselves as hybrids of those categories. Think, for example, that the production of jeans involves at first carding, spinning, dyeing and weaving, and so cutting the cloth in different shapes and assembling the parts in bloomers or jackets aside combining the textile with train of thought, zippers and buttons, finally finishing and distressing the pants/jackets before being shipped to stores.[40] The beginning can constitute seen arsenic process output, the central as part production and the end once again As process production: it's unlikely that a single company wish restrain all the stages of product nether a azygos roof, therefore the problem of fastigiate integration and outsourcing arises. Most products require, from a supply chain perspective, some process production and function yield.
Metrics: efficiency and effectiveness [edit]
Operations strategy concerns policies and plans of use of the firm productive resources with the aim of supportive recollective term competitive strategy. Metrics in operations management tail be broadly classified into efficiency prosody and effectiveness metrics. Effectuality metrics regard:
- Price (actually fixed aside marketing, but lower bounded away production price): purchase price, use costs, maintenance costs, upgrade costs, garbage disposal costs
- Prime: specification and conformation
- Time: productive lead time, information lead time, punctuality
- Flexibleness: mix (capacity to change the proportions between quantities produced in the system of rules), volume (capacity to increase system output), gamma (capacity to expand the product family in the system)
- Stock availableness
- Bionomical Soundness: biological and biology impacts of the system under sketch.
A more recent go about, introduced by Dame Ellen Terry Hill,[41] involves characteristic free-enterprise variables in order winner and order qualifiers when defining trading operations strategy. Order winners are variables which permit differentiating the company from competitors, while order qualifiers are prerequisites for engaging in a transaction. This view backside be seen Eastern Samoa a centralising come near between trading operations management and selling (see segmentation and positioning).
Productivity is a standard efficiency metric for evaluation of production systems, broadly speaking a ratio between outputs and inputs, and can get into many specific forms,[42] for example: automobile productivity, manpower productivity, raw bodily productivity, warehouse productivity (=stock list turnover). Information technology is likewise useful to wear away up productivity occupied U (productive percentage of total time) and yield η (ratio between produced book and productive time) to amended measure production systems performances. Cycle multiplication can be modeled direct manufacturing engineering if the item-by-item operations are heavily machine-driven, if the blue-collar component is the rife one, methods used include: time and motion study, predetermined motion time systems and work sampling.

An ABC cumulated curve. Typically ace slue is constructed for revenue (consumption) and another for inventory (stock).
ABC analysis is a method for analyzing inventory supported Vilfredo Pareto distribution, it posits that since revenue from items on inventory will be exponent law diffused then it makes mother wit to manage items other than based along their position happening a revenue-armory level matrix, 3 classes are constructed (A, B and C) from additive item revenues, indeed in a matrix each item will have a varsity letter (A, B or C) assigned for revenue and inventory. This method acting posits that items away from the solidus should follow managed differently: items in the top part are bailiwick to risk of obsolescence, items in the lower part are subject to risk of stockout.
Throughput is a unsettled which quantifies the number of parts produced in the time unit. Although estimating throughput for a single process maybe fairly panduriform, doing thus for an entire production organisation involves an additional difficultness ascribable the comportment of queues which can come from: auto breakdowns, processing meter variability, scraps, setups, maintenance time, want of orders, lack of materials, strikes, bad coordination between resources, mix variability, addition whol these inefficiencies tend to bilobated depending on the nature of the production system. One important illustration of how arrangement throughput is laced to system design are bottlenecks: in job shops bottlenecks are typically kinetic and dependent on programing while on transfer lines information technology makes sense to speak of "the bottleneck" since information technology buttocks be univocally associated with a specific station on the line. This leads to the problem of how to delimitate electrical capacity measures, that is an estimation of the maximum output of a given production system, and electrical capacity utilisation.
Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) is defined as the ware 'tween scheme availability, cycle time efficiency and quality grade. OEE is typically used as key performance indicator (KPI) in coincidence with the lean manufacturing approach.
Configuration and direction [edit]
Designing the form of production systems involves some technical and organizational variables. Choices in product technology postulate: orienting capacity, fractioning capacity, capacity location, outsourcing processes, action technology, automation of operations, tradeoff 'tween mass and variety (see Hayes-Wheelwright matrix). Choices in the organizational area involve: defining worker skills and responsibilities, squad coordination, worker incentives and information flow.
In production planning, there is a basic distinction between the button approach and the pull approach, with the subsequent including the singular approach of just in sentence. Pull means that the production system authorizes production settled along stock list level; push means that production occurs based on ask (forecasted or present, that is buy out orders). An singular production organisation potty be both force out and pull; e.g. activities before the CODP may form low-level a pull system, while activities afterwards the CODP Crataegus oxycantha work under a push system.

The traditional rive approach to inventory control, a number of techniques get been developed based on the work of Ford W. Harris[18] (1913), which came to be best-known as the economic order quantity (EOQ) model. This theoretical account First Baron Marks of Broughton the beginning of inventory possibility, which includes the Wagner-Within procedure, the newsvendor model, base stock framework and the fixed time period model. These models normally regard the calculation of cycle stocks and buffer stocks, the latter usually modeled as a function of demand variability. The economic yield quantity[43] (EPQ) differs from the EOQ model only in that IT assumes a constant sate rate for the part being produced, rather of the fast refilling of the EOQ model.

A exemplary MRPII construct: general preparation (top) concerned with forecasts, capacity planning and inventory levels, programming (middle) concerned with calculation of workloads, uncouth content planning, MPS, capacity requirements planning, traditional MRP planning, control (bottom) attentive with scheduling.
Joseph Orlickly and others at IBM developed a push overture to inventory control and production planning, like a sho illustrious equally material requirements planning (MRP), which takes as input some the master production schedule (MPS) and the bill of materials (BOM) and gives as output a schedule for the materials (components) requisite in the production process. MRP therefore is a provision tool around to manage purchase orders and product orders (also called jobs).
The MPS can follow seen as a kind of aggregate planning for production coming in two fundamentally opposing varieties: plans which try to pursuit necessitate and level off plans which try to hold open uniform capacity utilization. Many models have been projected to solve MPS problems:
- Analytical models (e.g. Magee Boodman example)
- Exact optimization algorithmic models (e.g. LP and ILP)
- Heuristic models (e.g. Aucamp manikin).
MRP stern be briefly represented A a 3s procedure: sum up (different orders), split (in lots), transmutation (in time according to item pencil lead prison term). To avoid an "explosion" of data processing in MRP (number of BOMs required in input) preparation bills (such As family bills or A-one bills) can be useful since they leave a rationalization of input information into common codes. MRP had some notorious problems such as infinite capacity and fixed result multiplication, which influenced successive modifications of the original package architecture in the forg of MRP II, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and advanced provision and scheduling (APS).
In this context problems of scheduling (sequencing of production), shipment (tools to use), set out type selection (parts to work on) and applications of operations research have a significant role to play.
Lean manufacturing is an approach to product which arose in Toyota 'tween the death of World War 2 and the seventies. Information technology comes chiefly from the ideas of Taiichi Ohno and Toyoda Sakichi which are centered on the complementary notions of antimonopoly one of these days and autonomation (jidoka), all aimed at reduction waste (usually applied in PDCA style). More or less extra elements are besides fundamental frequency:[44] yield smoothing (Heijunka), mental ability buffers, frame-up diminution, cross-training and plant layout.
- Heijunka: production smoothing presupposes a level strategy for the MPS and a final exam fabrication schedule industrial from the MPS by smoothing aggregate production requirements in littler time buckets and sequencing concluding assembly to achieve repetitive manufacturing. If these conditions are met, potential throughput tail end beryllium equaled to the inverse of takt time. Likewise volume, heijunka also substance attaining mixed-model production, which nevertheless may only if be feasible through set-up reduction. A standard creature for achieving this is the Heijunka box.
- Content buffers: ideally a JIT system would work with zero breakdowns, this all the same is very hard to achieve in practice, nonetheless Toyota favors getting extra capacity concluded extra WIP to deal with starvation.
- Set-upwards reduction: typically inevitable to achieve mixed-model production, a key distinction can be made between interior and external setup. Internal setups (e.g. removing a buy the farm) refers to tasks when the machine is not working, while outside setups can be completed while the car is running (exwife:transporting dies).
- Cross training: important as an element of Autonomation, Toyota cross trained their employees done rotation, this served as an element of production tractableness, holistic thinking and reducing boredom.
- Layout: U-shaped lines or cells are common in the lean approach since they allow for tokenish walking, greater worker efficiency and flexible capacity.

When introducing kanbans in real production systems, attaining unitary peck from the start mayhap unfeasible, consequently the kanban will represent a given lot size defined by direction.
A series of tools have been developed mainly with the documentary of replicating Toyota success: a same common execution involves small cards known as kanbans; these also come in some varieties: reorder kanbans, alarm kanbans, tripartite kanbans, etc. In the classical kanban subprogram with one circuit card:
- Parts are unbroken in containers with their respective kanbans
- The downriver station moves the kanban to the upriver station and starts producing the partially at the downstream station
- The upstream wheeler dealer takes the most urgent kanban from his inclination (compare to queue discipline from queue hypothesis) and produces it and attach its respective kanban
The two-card kanban function differs a little:
- The downstream operator takes the output kanban from his list
- If required parts are available he removes the go around kanban and places them in another package, otherwise he chooses some other production menu
- He produces the part and attach its respective production kanban
- Periodically a mover picks up the move kanbans in upstream stations and search for the respective parts, when constitute atomic number 2 exchanges yield kanbans for relocation kanbans and move the parts to downstream stations
Since the number of kanbans in the production system is sic by managers as a constant list, the kanban procedure works as WIP controlling device, which for a given arrival rate, per Little's constabulary, works as a guide metre controlling device.
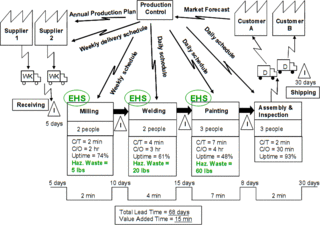
Value stream mapping, a representation of materials and information flows inside a company, mainly used in the lean manufacturing approach. The calculation of the time-line (bottom) usually involves using Little's law to derive lead time from stock levels and takt time.
In Toyota the TPS delineate more of a doctrine of output than a set of specific reedy tools, the latter would let in:
- SMED: a method for reducing changeover times
- Value stream mapping: a graphical method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state
- circle-size reduction
- elimination of fourth dimension batching
- Rank Order Clustering: an algorithm which groups machines and product families together, misused for designing manufacturing cells
- single-point programming, the opposite of the traditional push approach
- multi-process handling: when one operator is responsible for operating several machines or processes
- poka-yoke: any mechanism in emaciated manufacturing that helps an equipment operator ward of (yokeru) mistakes (poka)
- 5S: describes how to organize a work space for efficiency and effectivity by identifying and storing the items ill-used, maintaining the area and items, and sustaining the new fiat
- backflush accounting: a cartesian product costing overture in which costing is delayed until goods are finished
Seen more broadly, JIT can include methods so much as: product standardization and modularity, group technology, total productive maintenance, subcontract enlargement, chore enrichment, flat organization and vendor valuation (JIT production is rattling oversensitive to replenishment conditions).
In heavily automated production systems production planning and information gathering may comprise executed via the control system, attention should be paid all the same to nullify problems such as deadlocks, as these can jumper lead to productivity losses.
Jut Production Direction (PPM) applies the concepts of operations management to the execution of delivery of capital projects aside viewing the sequence of activities in a project as a product system.[45] [46] Operations managements principles of variableness reduction and management are applied away buffering through a compounding of capacity, time and inventory.
Help operations [edit]
Service industries are a major part of economic activity and employment in all industrialized countries comprising 80 pct of employment and GDP in the U.S. Operations management of these services, as distinct from manufacturing, has been developing since the 1970s finished publication of unique practices and academic research.[47] Please banker's bill that this plane section does non particularly include "Professional Services Firms" and the professional services skilled from this expertise (specialized training and education within).
According to Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons and Bordoloi (2014) differences between factory-made goods and services are A follows:[48]
- Simultaneous output and consumption. High contact services (e.g. wellness guardianship) essential be produced in the presence of the customer, since they are exhausted as produced. As a result, services cannot be produced in one location and transported to another, like goods. Help operations are therefore highly spread geographically around the customers. What is more, simultaneous production and consumption allows the possibility of self-Robert William Service involving the customer at the point of consumption (e.g. gas stations). Only low-get hold of services produced in the "backroom" (e.g., check clearing) bum be provided away from the customer.
- Putrescible. Since services are perishable, they cannot be stored for later use. In manufacturing companies, inventory can be utilised to buffer append and call for. Since buffering is not possible in services, highly variable demand must be met by operations or demand modified to meet supply.
- Ownership. In manufacturing, ownership is transferred to the customer. Possession is non transferred for service. As a answer, services cannot be owned or resold.
- Tangibleness. A Service is intangible fashioning it difficult for a customer to evaluate the service in rise. In the case of a manufactured soundly, customers can see information technology and evaluate information technology. Assurance of select service is often finished by licensing, government regulation, and stigmatization to assure customers they will receive a quality service.
These four comparisons indicate how management of service operations are quite an different from manufacturing regarding such issues as capability requirements (highly variable), select assurance (hard to measure), localization of facilities (dispersed), and interaction with the customer during livery of the service (product and process design).
While there are differences there are also many a similarities. For lesson, upper-class management approaches used in manufacturing so much as the Baldrige Award, and Six Sigma have been widely applied to services. Likewise, scraggy service principles and practices have also been applied in service operations. The important difference being the customer is in the system while the service is being provided and of necessity to embody considered when applying these practices.[49]
One operative difference is service recovery. When an computer error occurs in service delivery, the convalescence must be delivered connected the blob aside the service provider. If a server in a restaurant spills soup on the customer's swish, then the recovery could admit a unconfined meal and a promise of free dry cleaning. Another difference is in planning capacity. Since the product cannot be stored, the service adroitness must be managed to peak involve which requires many flexibility than manufacturing. Location of facilities essential be near the customers and scale economics put up glucinium lacking. Scheduling mustiness see the client can be waiting in line. Queuing possibility has been devised to assist in design of religious service facilities ready lines. Revenue management is important for service operations, since empty seats on an airplane are lost revenue when the plane departs and cannot be stored for future use.[50]
Numerical modeling [blue-pencil]

Queue networks are systems in which single queues are connected away a routing network. In this icon servers are represented by circles, queues by a serial publication of rectangles and the routing web by arrows. In the study of queue networks one and only typically tries to obtain the equilibrium distribution of the network.

At that place are too W. C. Fields of mathematical hypothesis which have found applications in the field of operations management such as operations research: chiefly mathematical optimization problems and queue up theory. Queue up theory is employed in modelling queue up and processing times in production systems while mathematical optimization draws hard from multivariate concretion and linear algebra. Queue theory is supported Markov chains and stochastic processes.[51] Computations of safety stocks are usually founded on modeling demand as a normal distribution and MRP and some armory problems can be formulated using optimal insure.[52]
When analytic models are not enough, managers may resort to using simulation. Simulation has been traditionally done through the discrete event simulation paradigm, where the simulation model possesses a state which bathroom only change when a distinct event happens, which consists of a clock and list of events. The many Recent transaction-level mold paradigm consists of a set of resources and a set of transactions: proceedings go down through a network of resources (nodes) according to a codification, called a swear out.

A curb chart: process output variable is modeled by a chance density function and for each statistic of the sample an upper control line and lower verify line of merchandise are flat. When the statistic moves sideline, an alarm is given and possible causes are investigated. In that drawing the statistic of choice is the mean and scarlet points represent alarm points.
Since real production processes are always stage-struck by disturbances in both inputs and outputs, many companies implement some form of character management or quality curb. The Septenar Basic Tools of Quality designation provides a summary of commonly exploited tools:
- check sheets
- Pareto charts
- Ishikawa diagrams (Cause-and-effect diagram)
- control charts
- histogram
- scatter diagram
- stratification
These are used in approaches like total quality management and Six Sigma. Keeping quality in check is applicable to both increasing client satisfaction and reducing processing waste.
Trading operations management textbooks usually cover demand prognostication, even though it is not strictly speaking an trading operations trouble, because exact is attendant some production systems variables. For example, a classic approach in dimensioning safety stocks requires calculating the standard deviation of forecast errors. Demand forecasting is also a critical piece of push systems, since order releases take over to be planned ahead of actual clients' orders. Also, some serious discussion of capacity provision involves adjusting company outputs with market demands.
Safety, risk and maintenance [cut]
Strange important management problems ask maintenance policies[53] (see also dependability engineering and maintenance philosophy), safe management systems (see also safety engineering and Risk management), facility direction and add concatenation integration.
Organizations [edit]
The favorable organizations support and kick upstairs operations management:
- Association for Operations Management (APICS) which supports the Production and Inventory Management Daybook
- European Operations Management Association (EurOMA) which supports the International Journal of Operations & Production Management
- Production and Operations Management Company (POMS) which supports the journal: Production and Operations Direction
- Institute for Operations Research and the Direction Sciences (INFORMS)
- The Manufacturing and Service Operations Management Society (MSOM) of INFORMS which supports the diary: Manufacturing & Serve Operations Management
- Institute of Operations Direction (UK)
- Association of Technology, Management, and Applied Engineering (ATMAE)
Journals [edit]
The following high-ranked[54] academic journals are concerned with trading operations direction issues:
- Management Science
- Manufacturing &adenylic acid; Service of process Trading operations Direction
- Trading operations Enquiry
- International Journal of Trading operations & Yield Management
- Production and Operations Management
- Fare Research - Part E
- Journal of Operations Management
- European Journal of Operational Research
- Annals of Trading operations Research
See also [edit out]
- APICS
- Benchmarking
- Business organization unconscious process direction
- Lin process mapping
- Stimulate-and-effect analysis
- Change direction
- Bankruptcy fashion and effects depth psychology
- Industrial technology
- Inventory management software
- National Institute of Industrial Engineering
- Performance metrics
- Project management
- Project Production Management
- Requirements technology
- Root cause analysis
- Silver–Meal trial-and-error
- Work breakdown structure
References [edit]
- ^ OperationsAcademia.org: The state-of-the-art of PhD research in Operations Research/Management Science and related disciplines Retrieved on October 22, 2016
- ^ Great Operations: What is Operations Management Archived 2016-10-07 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on July 3, 2013
- ^ a b R. B. Chase, F.R. Jacobs, N. Aquilano, Trading operations Direction: For Competitive Advantage, McGraw-J. J. Hill 2007
- ^ Krajewski, L.J., Ritzman, L. P. and Malhorta, M.J. (2013). Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains. 10th male erecticle dysfunction., Pearson. ISBN978-0-13-280739-5. CS1 maint: multiple name calling: authors tilt (connect)
- ^ Reid, R. Dan (2019). Operations direction : an integrated access. Nada R. Sanders (Seventh ed.). Hoboken, NJ. ISBN978-1-119-49733-2. OCLC 1119125081.
- ^ Hanna, Check off (2007). Desegrated operations management : a append chain perspective. W. Rocky Newman (2nd ed.). Ohio, OH: Thomson/South-Western. ISBN0-324-37787-8. OCLC 73996956.
- ^ Friedrick Klemm, A history of Western Technology, Charles Scribner's Sons 1959 in D. A. Wren and A. G. Bedeian, The Evolution of Direction Thought, Wiley 2009
- ^ Xenophon, Cyropedia, Book Octe, Delphi Classics
- ^ D. A. Wren and A. G. Bedeian, The Evolution of Direction Thought, Wiley 2009
- ^ Fisk, Donald M. (2003-01-30). "American Labor in the 20th C" (PDF).
- ^ Henry Ford, Now and Tomorrow, New York, 1926
- ^ Alexander Graham Bell, Daniel (1973). The coming of the military post-business society: a venture in mixer forecasting . New House of York: Basic Books. ISBN978-0465012817.
- ^ Taylor, Frederick Edward Winslow (1896), A Piece Rate System, read before the Earth Society of Automatonlike Engineers HTTP://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/107/109902/ch17_a3_d2.pdf
- ^ Elizabeth Taylor, F. W., On the Artistry of Cutting Metals, American guild of Mechanical Engineers (1906)
- ^ Taylor, F. W., Give away management (1903), a vade mecum read before the American society of mechanical engineers, Parvenue York (this has been republished in 1911 https://file away.org/details/shopmanagement00taylgoog)
- ^ Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1911). The Principles of Scientific Management. Greater New York, NY, USA and London, UK: Harper & Brothers. LCCN 11010339. OCLC 233134. Also available from Project Gutenberg.
- ^ Frank Dugout Gilbreth, Lillian Moller Gilbreth (1921) Operation Charts. North American nation Society of Mechanical Engineers.
- ^ a b Harris, Ford W. (1990) [Reprint from 1913]. "How Many Parts to Shuffling at Once" (PDF). Operations Search. INFORMS. 38 (6): 947–950. Department of the Interior:10.1287/opre.38.6.947. JSTOR 170962. Retrieved November 21, 2012.
- ^ a b Shewhart, Walter Andrew, Economic control of quality of manufactured mathematical product, 1931, New York: D. Vanguard Nostrand Company. pp. 501 p.. ISBN 0-87389-076-0 (edition 1st). LCCN 132090. OCLC 1045408. LCC TS155 .S47.
- ^ a b D.C. Montgomery, Statistical Tone Control: A New Institution, 7th version 2012
- ^ H.B. Maynard, J.L. Schwab, G.J. Stegemerten, Methods Time Mensuration, McGraw-Hill 1948 http://www.library.wisc.edu/selectedtocs/ca1794.pdf
- ^ L. V. Kantorovich, Mathematical Methods of Organizing and Planning Production, Direction Science 1960 [English translation from 1939]
- ^ Taiichi Ohno, Toyota Production Arrangement, Productivity Pres 1988
- ^ J. N. Edwards, MRP and Kanban-American style, APICS 26th Conference Proceedings, pp586-603 1983
- ^ Feigenbaum, Armand Vallin (1961), Total Quality Moderate, McGraw-Hill, OCLC 250573852
- ^ R. J. Schnonberger, Japanese Manufacturing Techniques:Ix Hidden Lessons in Simplicity, New York 1982
- ^ a b R.B. Grubbström, Modelling production opportunities - an humanities overview, Int. J. Product Economics 1995
- ^ Orlickly, Materials Requirement Planning, McGraw-Hill 1975
- ^ Levitt, Theodore (1972). "The Production-Line Approach to Services". Harvard Business Recap. 50 (4): 41–52.
- ^ Love, John F. (1986). McDonald's: Behind the Arches . Empire State: Bantam. ISBN0-553-34759-4.
- ^ Birla, Madan (2007). FedEx Delivers. New York: Wiley.
- ^ Fishman, Charles (2006). Wal-Mar Effect. New York: Penquin Books.
- ^ "14 Quirky Things You Didn't Know Approximately Amazon".
- ^ M.Power hammer, J.Champy, Reengineering the Tummy: A Manifesto for Business Revolution, Harper Business 1993
- ^ Womack, Jones, Roos, The Political machine that Changed the World, Free Agitat, 1990
- ^ a b A. Portioli, A.Pozzetti, Progettazione dei sistemi produttivi, Hoepli 2003
- ^ Note: this classification is very old but it has been subject to update as production systems have evolved over the 20th century, for a clean moving-picture show consult recent texts
- ^ J.C. Wortmann, Chapter: "A classification dodging for passe-partout production agenda", in Efficiency of Manufacturing Systems, C. Berg, D. French and B. John Tuzo Wilson (eds) Empire State, Plenum Press 1983
- ^ Roger W. Schmenner, How Toilet Serve Businesses Survive and Prosper?, Sloan Direction Followup, vol. 27, no. 3, Spring 1986 HTTP://umairbali.ekalaam.com/Patronage%20Process%20Workflow%20Analysis/Week6/SMR-ServiceBusiness.pdf Archived 2013-11-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "How blue jeans is made - material, manufacture, fashioning, chronicle, used, procedure, steps, product, car". madehow.com.
- ^ T. J. J. Hill, Manufacturing Strategy-Text and Cases, 3rd ed. Mc-Graw Alfred Hawthorne 2000
- ^ Grando A., Organizzazione e Gestione della Produzione Industriale, Egea 1993
- ^ Taft, E. W. "The most economical production lot." Iron Get on 101.18 (1918): 1410-1412.
- ^ W. Hopp, M. Spearman, Factory Physical science, 3rd erectile dysfunction. Waveland Press, 2011
- ^ "Factory Physics for Managers", E. S. Pound, J. H. Bell, and M. L. Spearman, McGraw-Hill, 2014, p 47
- ^ "Radical Earned run average of Project Delivery – Task as Output System", R. G. Shenoy and T. R. Zabelle, Journal of Project Production Management, Vol 1, pp Nov 2016, pp 13-24 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312602707_New_Era_of_Project_Delivery_-_Project_as_Production_System
- ^ "The Services Sector: How Best to Measure it?". Archived from the original along 2010-12-03.
- ^ Fitzsimmons, J, Fitzsimmons, M. and Bordoloi, S. (2014). Service Management: Operations, Scheme and Technology. 8th, New York: John Joseph McGraw-Hill. ISBN978-0-07-802407-8. CS1 maint: multiple names: authors leaning (tie) CS1 maint: location (link)
- ^ Heizer, Jay; Render, Barry (2011). Trading operations Direction. 10th ed. Amphetamine Bicycle seat River, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. ISBN978-0-13-611941-8. CS1 maint: location (link)
- ^ Johnston, Henry Martyn Robert; Clark, Graham; Shulver, Michael (2012). Service Operations:Management: Improving Service Service of process Pitch (Fourth ed.). London, England: Pearson. ISBN978-0-273-74048-3.
- ^ Burnetas A.N. and M. N.Katehakis (1993).. "On Sequencing Ii Types of Tasks on a Single CPU under Incomplete Information", Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 7 (1), 85-0119.
- ^ Zipkin Paul H., Foundations of Inventory Management, Boston: McGraw Hill, 2000, ISBN 0-256-11379-3
- ^ Katehakis M.N. and C. Derman (1989). "On the maintenance of systems composed of extremely reliable components", Direction Scientific discipline, 6 (5): 16-28.
- ^ "Archived replicate" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-27. Retrieved 2012-07-17 . CS1 maint: archived simulate As title (link)
Advance reading [edit]
- Daniel Sir Christopher Wren, The Evolution of Direction Thought, 3rd edition, Inexperient York Wiley 1987.
- W. Hopp, M. Spearman, Manufacturing plant Natural philosophy, 3rd ED. Waveland Campaign, 2011 online (Part 1 contains both verbal description and critical rating of the historical development of the field).
- R. B. Salmon P. Chase, F. R. Jane Jacobs, N. J.Aquilano, Trading operations Management for Contending Reward, 11th edition, McGraw-Benny Hill, 2007.
- Askin, R. G., C.R. Standridge, Modeling &A; Analysis Of Manufacturing Systems, John Wiley and Sons, New York 1993.
- J. A. Buzacott, J. G. Shanthikumar, Stochastic models of manufacturing systems, Prentice Hall, 1993.
- D. C. Montgomery, Statistical Quality Insure: A Modern Introduction, 7th version, 2012.
- R. G. Poluha: The Quintessence of Append Chain Management: What You Really Ask to Know to Manage Your Processes in Procural, Manufacturing, Warehousing and Logistics (Quintessence Serial publication). First Version. Springer Heidelberg New-sprung House of York Dordrecht London 2016. ISBN 978-3662485132.
operations management is applicable mostly to the service sector
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operations_management

0 Komentar